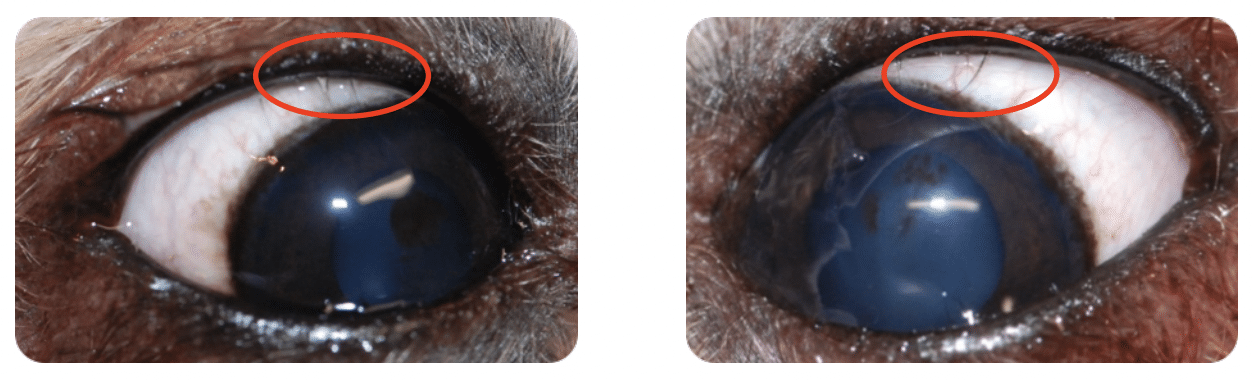
Distichiasis are extra, abnormally positioned hairs (cilia) along the eyelid margin. These cilia can cause irritation to the eye because they are directed toward, instead of away from the eye surface. Many dogs go through life with distichiasis hairs and if few in number, usually cause minimal to no problems. Eyes irritated by distichiasis usually have intermittent or persistent redness, squinting, and increased tearing and are prone to corneal ulceration and scarring. When distichiasis are identified to be causing ocular irritation, the hairs should be removed so they do not cause permanent damage to the cornea.
Cryoepilation involves freezing distichiasis follicles in the eyelid margin with an ophthalmic cryosurgical unit. This technique is especially beneficial when several distichiasis are present, and is associated with the most predictable healing post-operatively. Side effects include temporary swelling of the eyelid and depigmentation (pigment loss) of the eyelid margins. Repigmentation of the eyelid margins is usually complete within 4-6 months of surgery. Cryoepilation is effective in destroying 75-85% of hair follicles in a single treatment. In dogs with numerous distichiasis, and especially those under 2 yrs of age, more hairs can grow following surgery. In these cases, a second surgical procedure is required to relieve irritation from new hairs.
Electrolysis involves burning distichiasis follicles in the eyelid margin with an ophthalmic electrolytic unit. This technique is especially beneficial when several distichiasis are present, and is associated with the most predictable healing post-operatively. There is no major side effect. Electrolysis is effective in destroying 75-85% of hair follicles in a single treatment. In dogs with numerous distichiasis, and especially those under 2 years of age, more hairs can grow following surgery. In these cases, a second surgical procedure is required to relieve irritation from new hairs.

Electrolysis tip: a very thin metallic tip that can be inserted in the base of the hair follicle.
The surgical alternative consists in removing a strip of the palpebral conjunctiva that contains the hair follicles. This technique is especially beneficial when several distichiasis are present. This technique is more invasive but it is effective in destroying most of hair follicles in a single treatment.